guage. Before we consider the relevant clinical and
anatomical studies, we shall first review the overall
structure of the brain. (The anatomical organization
of the nervous system is described in some detail in
Chapter 17.)
abolic activity of discrete regions of the brain while
people are engaged in specific tasks under controlled
conditions. Such studies provide direct evidence that
specific types of behavior involve particular regions of
the brain. As a result, Gall’s original idea that discrete
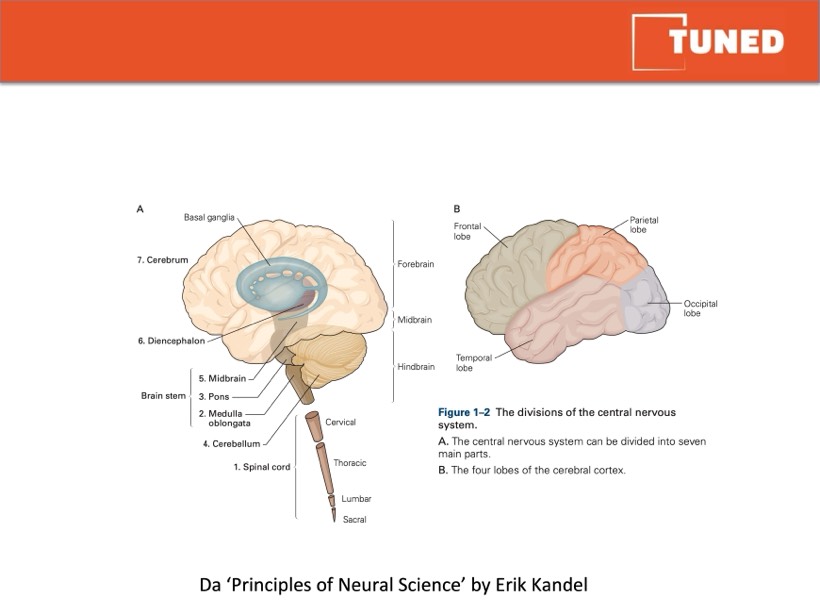
A
Basal ganglia
B
Frontal
lobe
Midbrain
Temporal
Parietal
lobe
7. Cerebrum
6. Diencephalon
Forebrain
Brain stem
5. Midbrain
3. Pons
2. Medulla
oblongata
4. Cerebellum
1. Spinal cord
Cervical
Thoracic
Lumbar
Sacral
Figure 1–2 The divisions of the central nervous
system.
Da ‘Principles of Neural Science’ by Erik Kandel
Hindbrain
lobe
A. The central nervous system can be divided into seven
main parts.
B. The four lobes of the cerebral cortex.
Occipital
lobe